Wizardlib¶
Here, you'll find the documentation for CodeWizardHQ's Wizardlib Python library. We use this library in the following courses:
| Elementary | Middle School | High School |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Fundamentals with Python | Introduction to Programming with Python | Intro to Python |
| Logic with Python | Wizard Level 1 Capstone | |
| Modular Programming with Python | ||
| Wizard Level 2 Capstone | ||
| Python Game Development |
add_audio()¶
Adds an audio file.
Function signature:
add_audio(filename)
Parameters:
filename(str) : The filename.
Returns:
- The audio element.
Example usage:
audio_element = add_audio("never-gonna-give-you-up.mp3")
add_background()¶
Adds a background image.
Function signature:
add_background(filename)
Parameters:
filename(str): The filename.
Example usage:
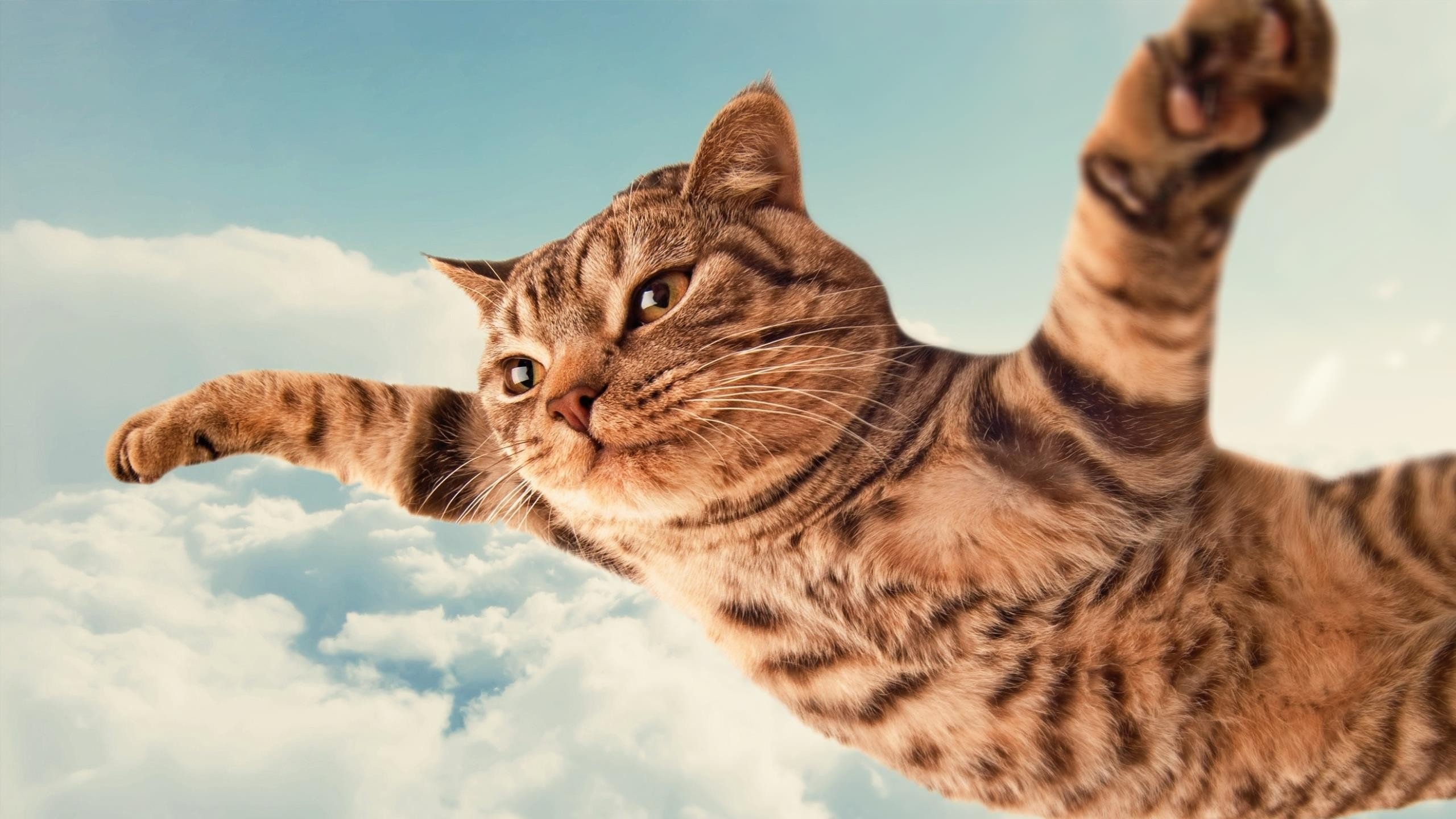
add_background("flying-cats.png")
Example output:

add_background_audio()¶
Adds background audio which plays when you click the Start button.
Function signature:
add_background_audio(filename)
Parameters:
filename(str): The filename.
Example usage:
add_background_audio("never-gonna-give-you-up.mp3")
add_button()¶
Adds a button.
Function signature:
add_button(text)
Parameters:
text(str): The text on the button.
Returns:
- The button element.
Example usage:
button = add_button("Click Me")
Example output:

add_image()¶
Adds an image to the page.
Function signature:
add_image(filename, size)
Parameters:
filename(str): The filename.size(int): The size, in pixels (optional).
Returns:
- The image element.
Example usage:
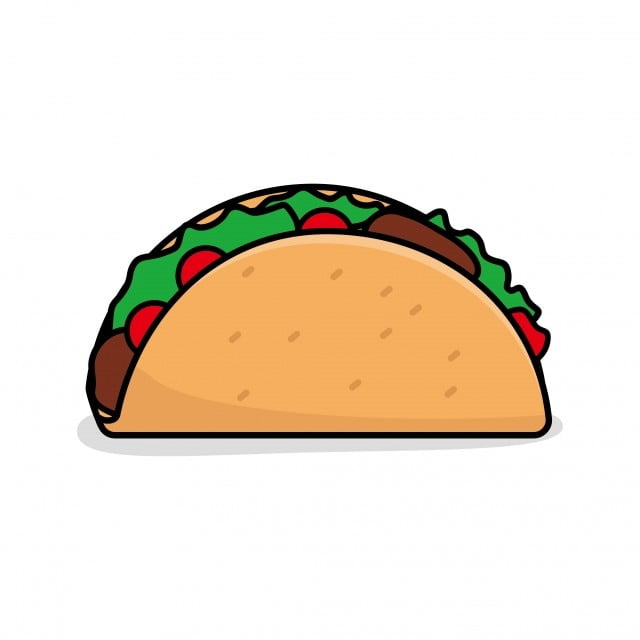
taco_image = add_image("taco.png")
Example output:

add_text()¶
Adds text to the page.
Function signature:
add_text(text, size)
Parameters:
text(str): The text to add to the page.size(int): The size, in pixels (optional, defaults to 18).
Returns:
- The text element.
Example usage:
wizardlib_text = add_text("Wizardlib is cool!")
Example output:

add_text_input()¶
Adds a text input to the page.
Function signature:
add_text_input(placeholder)
Parameters:
placeholder(str): The text to display in the input box.
Returns:
- The text input element.
Example usage:
text_input = add_text_input("Enter your password:")
Example output:

animate_down()¶
Animates the element down by the given distance. Can optionally change the amount of time the animation takes and whether the element animates down and up repeatedly.
Function signature:
animate_down(element, distance, time, loop)
Parameters:
element(element): An element to animate.distance(int): The distance the element should travel (in pixels).time(int): The amount of seconds the animation should take (optional, defaults to 8).loop(bool): Whether to repeatedly animate down and up (optional, defaults toFalse).
Example usage:
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg")
animate_down(taco_image, 100)
Example output:

animate_left()¶
Animates the element left by the given distance. Can optionally change the amount of time the animation takes and whether the element animates left and right repeatedly.
Function signature:
animate_left(element, distance, time, loop)
Parameters:
element(element): An element to animate.distance(int): The distance the element should travel (in pixels).time(int): The amount of seconds the animation should take (optional, defaults to 8).loop(bool): Whether to repeatedly animate left and right (optional, defaults toFalse).
Example usage:
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg")
animate_left(taco_image, 100)
Example output:

animate_right()¶
Animates the element right by the given distance. Can optionally change the amount of time the animation takes and whether the element animates right and left repeatedly.
Function signature:
animate_right(element, distance, time, loop)
Parameters:
element(element): An element to animate.distance(int): The distance the element should travel (in pixels).time(int): The amount of seconds the animation should take (optional, defaults to 8).loop(bool): Whether to repeatedly animate right and left (optional, defaults toFalse).
Example usage:
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg")
animate_right(taco_image, 100)
Example output:

animate_up()¶
Animates the element up by the given distance. Can optionally change the amount of time the animation takes and whether the element animates up and down repeatedly.
Function signature:
animate_up(element, distance, time, loop)
Parameters:
element(element): An element to animate.distance(int): The distance the element should travel (in pixels).time(int): The amount of seconds the animation should take (optional, defaults to 8).loop(bool): Whether to repeatedly animate up and down (optional, defaults toFalse).
Example usage:
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg")
animate_up(taco_image, 100)
Example output:

bound_element()¶
bound_element() allows you to keep an element, such as a piece of text or an image, inside of the screen while using animations or keyboard input.
Function signature:
bound_element(element)
Parameters:
element(element) : A text or image element you want to keep in the screen.
Example usage:
wizard = add_image("images/wizard.png", 100)
position_element(wizard, start_x, start_y)
bound_element(wizard)
Example output:

Note
bound_element() only works in lessons 1 thru 4 of the M14 Capstone course!
check_collision()¶
If element1 and element2 collide, function_to_run is called.
Function signature:
check_collision(element1, element2, function_to_run)
Parameters:
element1(element): An element to check for collisions with.element2(element): An element to check for collisions with.function_to_run(function): The function to run ifelement1hitselement2.
Example usage:
def cat_caught_taco():
clear()
text = add_text("The kitty caught the taco!")
position_element(text, "center", "center")
def move(key):
if key == "w":
move_up(cat_image, 10)
elif key == "a":
move_left(cat_image, 10)
elif key == "s":
move_down(cat_image, 10)
elif key == "d":
move_right(cat_image, 10)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 100)
position_element(taco_image, "center", "center")
cat_image = add_image("flying-cats.jpg", 100)
position_element(cat_image, 700, 300)
keydown(move)
check_collision(taco_image, cat_image, cat_caught_taco)
Example output:

clear()¶
Clear the page of all elements.
Function signature:
clear()
Example usage:
def clear_page():
clear()
after_clear_text = add_text("Page was cleared", 32)
position_element(after_clear_text, "center", "center")
before_clear_text = add_text("This is on the page before clearing", 32)
position_element(before_clear_text, "center", "center")
clear_page_button = add_button("Clear Page")
position_element(clear_page_button, "center", 400)
click(clear_page_button, clear_page)
Example output:

click()¶
Call function_to_run when element is clicked.
Function signature:
click(element, function_to_run)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to click.function_to_run(function): The function to run ifelementis clicked.
Example usage:
def show_text():
text = add_text("Button was clicked!", 32)
position_element(text, "center", "center")
button = add_button("Click Me")
position_element(button, "center", 400)
click(button, show_text)
Example output:

fade_in()¶
Fades the element from invisible to visible.
Function signature:
fade_in(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to fade in.
Example usage:
def fade_text_in():
fade_in(hidden_text)
hidden_text = add_text("Hidden Text", 32)
position_element(hidden_text, "center", 400)
fade_out(hidden_text)
fade_in_button = add_button("Fade In")
position_element(fade_in_button, "center", "center")
click(fade_in_button, fade_text_in)
Example output:
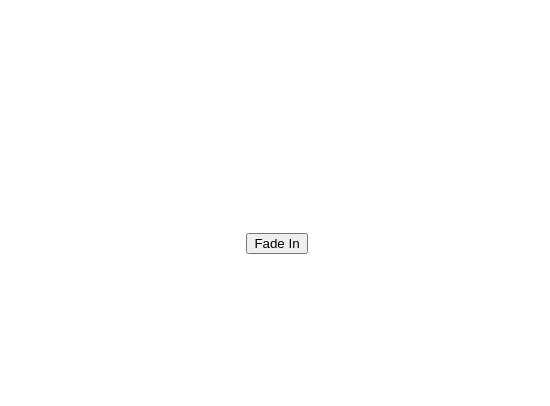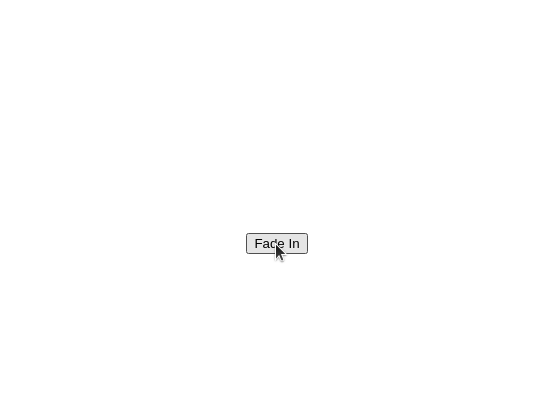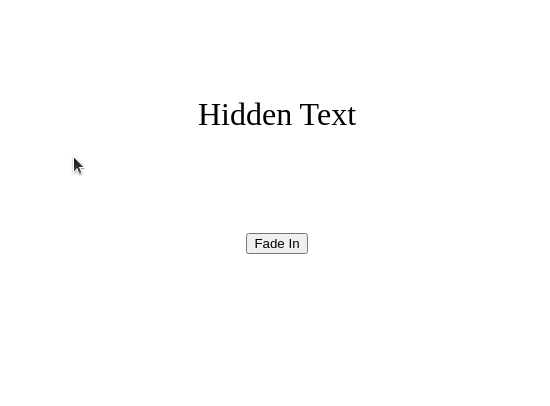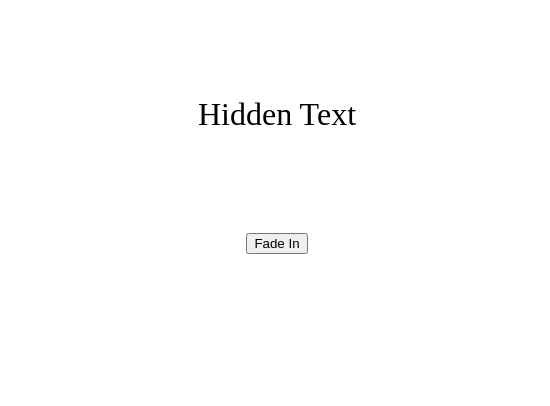
fade_out()¶
Fades the element from visible to invisible.
Function signature:
fade_out(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to fade out.
Example usage:
def fade_text_out():
fade_out(text_to_hide)
text_to_hide = add_text("Text To Hide", 32)
position_element(text_to_hide, "center", 400)
fade_out_button = add_button("Fade Out")
position_element(fade_out_button, "center", "center")
click(fade_out_button, fade_text_out)
Example output:

get_input_value()¶
Gets the value of the input element.
Function signature:
get_input_value(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to get the value from.
Example usage:
def login():
password = get_input_value(password_input)
clear()
if password == "secretpassword":
logged_in_text = add_text("You've logged in!", 32)
position_element(logged_in_text, "center", 400)
password_input = add_text_input("Enter your password")
position_element(password_input, "center", 400)
login_button = add_button("Login")
position_element(login_button, "center", "center")
click(login_button, login)
Example output:

jump()¶
Makes an image or text element move up and down (in a jumping motion).
Function signature:
jump(element, jump_height, time)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to make jump.jump_height(int): The height the element should jump.time(int): The time (in seconds) that the element will be in the air during the jump (optional, default is 2 seconds).
Example usage:
def make_jump(key):
if key == " ":
jump(robot, 100, 1)
robot = add_image("images/robot.png", 100)
position_element(robot, 600, 200)
keydown(make_jump)
Example output:

Note
jump() only works in E22: Logic with Python.
keydown()¶
Runs function_to_run when a key is pressed. The key that is pressed will be passed as the first argument to function_to_run and will always be lowercase.
Function signature:
keydown(function_to_run, fast=False)
Parameters:
function_to_run(function): The function to run when a key is pressed.fast(bool): Use this flag whenever you expect the user to quickly press and release keys for movement if you want smooth movement.
Note
The fast flag is only available in courses that use program.py as their main application file.
Example usage:
def key_logger(pressed_key):
update_text(last_key_pressed_text, f"Last key pressed: {pressed_key}")
last_key_pressed_text = add_text("Last key pressed: ", 32)
position_element(last_key_pressed_text, "center", 400)
keydown(key_logger)
Example output:

move_down()¶
Moves the element down by the given distance.
Function signature:
move_down(element, distance)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to move down.distance(int): The distance theelementshould travel (in pixels).
Example usage:
def move_taco(pressed_key):
if pressed_key == "w":
move_up(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "a":
move_left(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "s":
move_down(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "d":
move_right(taco_image, 10)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 100)
position_element(taco_image, "center", "center")
keydown(move_taco)
Example output:

move_left()¶
Moves the element left by the given distance.
Function signature:
move_left(element, distance)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to move left.distance(int): The distance theelementshould travel (in pixels).
Example usage:
def move_taco(pressed_key):
if pressed_key == "w":
move_up(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "a":
move_left(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "s":
move_down(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "d":
move_right(taco_image, 10)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 100)
position_element(taco_image, "center", "center")
keydown(move_taco)
Example output:

move_right()¶
Moves the element right by the given distance.
Function signature:
move_right(element, distance)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to move right.distance(int): The distance theelementshould travel (in pixels).
Example usage:
def move_taco(pressed_key):
if pressed_key == "w":
move_up(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "a":
move_left(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "s":
move_down(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "d":
move_right(taco_image, 10)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 100)
position_element(taco_image, "center", "center")
keydown(move_taco)
Example output:

move_up()¶
Moves the element up by the given distance.
Function signature:
move_up(element, distance)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to move up.distance(int): The distance theelementshould travel (in pixels).
Example usage:
def move_taco(pressed_key):
if pressed_key == "w":
move_up(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "a":
move_left(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "s":
move_down(taco_image, 10)
elif pressed_key == "d":
move_right(taco_image, 10)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 100)
position_element(taco_image, "center", "center")
keydown(move_taco)
Example output:

play_audio()¶
Plays the audio that element represents.
Function signature:
play_audio(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The audio element to play.
Example usage:
laugh_audio = add_audio("laugh.mp3")
play_audio(laugh_audio)
position_element()¶
Position the element at the given x and y position. The x and y arguments can be any int, or one of the position helpers:
| Position | Helper1 | Helper2 | Helper3 |
|---|---|---|---|
x |
"left" |
"center" |
"right" |
y |
"top" |
"center" |
"bottom" |
Function signature:
position_element(element, x, y)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to position.x(int|str): The desired x-position of theelement.y(int|str): The desired y-position of theelement.
Example usage:
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg")
position_element(taco_image, "center", 400)
set_background_color()¶
Sets the background color of the page to color.
Function signature:
set_background_color(color)
Parameters:
color(str): The desired background color.
Example usage:
set_background_color("darksalmon")
Example output:

set_element_width()¶
Sets the element to the given width.
Function signature:
set_element_width(element, width)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to adjust.width(int): The desired width of theelement.
Example usage:
def shrink_taco():
set_element_width(taco_image, 100)
shrink_taco_button = add_button("Shrink Taco")
position_element(shrink_taco_button, "center", "center")
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 300)
position_element(taco_image, "center", 200)
click(shrink_taco_button, shrink_taco)
Example output:

set_font_size()¶
Sets the font size of the element to the given font_size.
Function signature:
set_font_size(element, font_size)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to adjust.font_size(int): The desired font_size of theelement.
Example usage:
def shrink_text():
set_font_size(text_element, 25)
shrink_text_button = add_button("Shrink Font")
position_element(shrink_text_button, "center", "center")
text_element = add_text("Shrink this text!", 100)
position_element(text_element, "center", 300)
click(shrink_text_button, shrink_text)
Example output:

set_interval()¶
Runs function_to_run every time seconds.
Function signature:
set_interval(function_to_run, time)
Parameters:
function_to_run(function): The function to run.time(int): The time (in seconds) to wait before running thefunction_to_run.
Example usage:
def create_ship():
ship = add_image("ship.png", 100)
position_element(ship, 200, 100)
animate_right(ship, 2500, 10)
set_interval(create_ship, 3)
Example output:
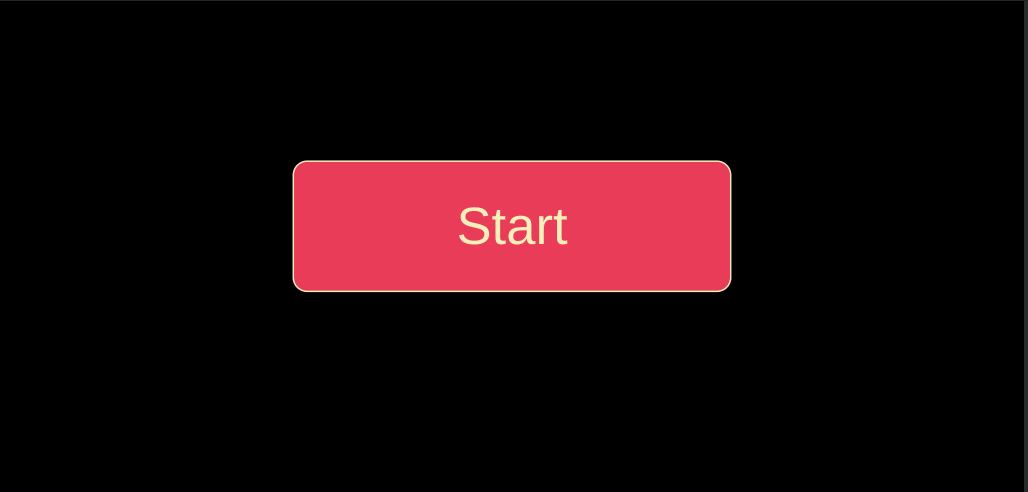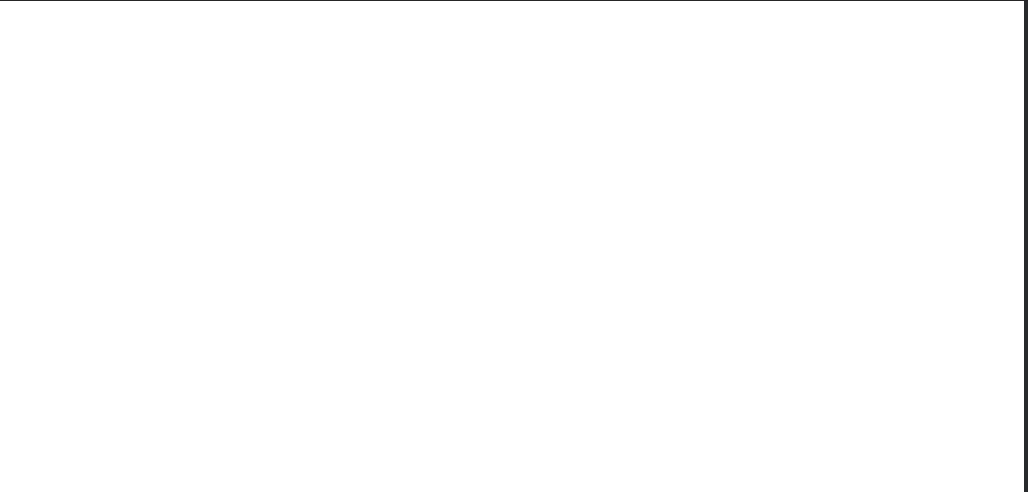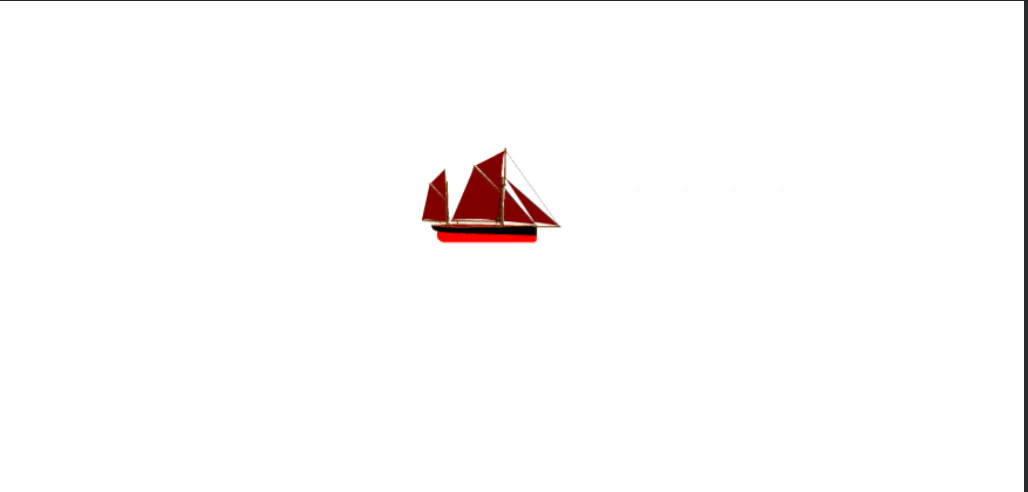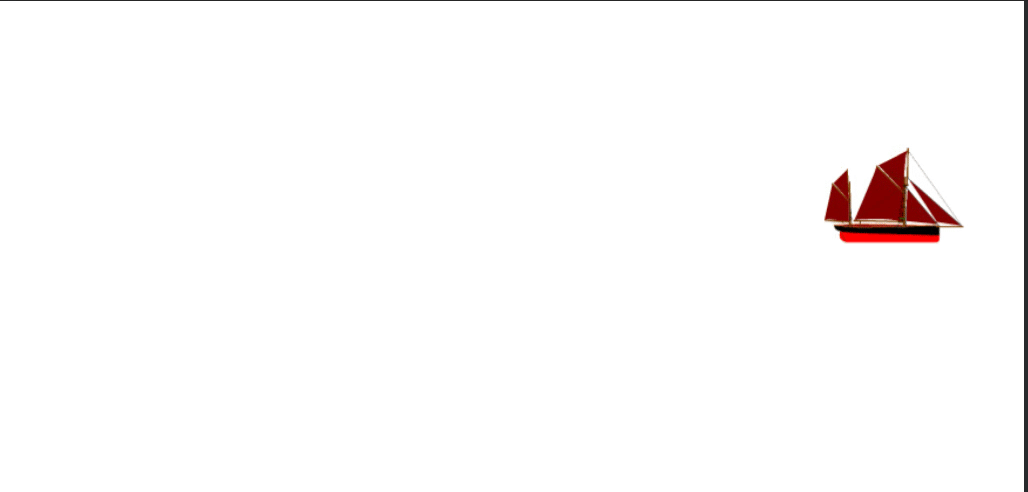
set_text_color()¶
Sets the color of the text_element.
Function signature:
set_text_color(text_element, color)
Parameters:
text_element(element): The text element to adjust.color(str): The desired color of thetext_element.
Example usage:
red_text = add_text("This text is red", 32)
set_text_color(red_text, "red")
Example output:

set_text_decoration()¶
Sets the text decoration of the given text_element.
Function signature:
set_text_decoration(text_element, decoration_string)
Parameters:
text_element(element): The text element to adjust.decoration_string(str): The decoration string for the CSS property.
Example usage:
text_element = add_text("Never Gonna Give You Up", 42)
set_text_decoration(text_element, "underline dotted blue")
Example output:
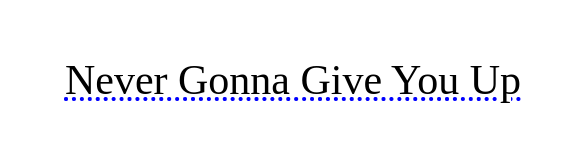
Read about different options for the decoration_string here
set_text_font()¶
This function allows you to change the font of a text element in your program.
Function signature:
set_text_font(text_element, font_name)
Parameters:
text_element(element): The text element to adjust.font_name(str): The font to use for thetext_element.
Example usage:
game_over = add_text("GAME OVER", 20)
position_element(game_over, "center", "center")
set_text_font(game_over, "game")
| Available Fonts |
|---|
| game |
| lora |
| quicksand |
| roboto |
| nabla |
Note
set_text_font() only works in E22: Logic with Python
set_timeout()¶
Runs function_to_run after time seconds.
Function signature:
set_timeout(function_to_run, time)
Parameters:
function_to_run(function): The function to run.time(int): The time (in seconds) to wait before running thefunction_to_run.
Example usage:
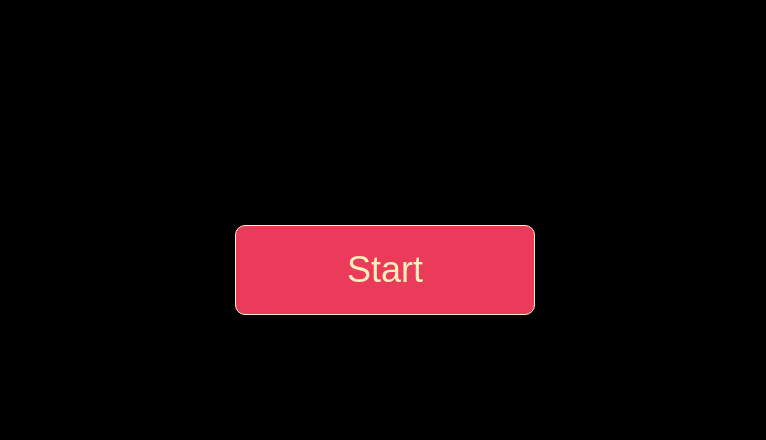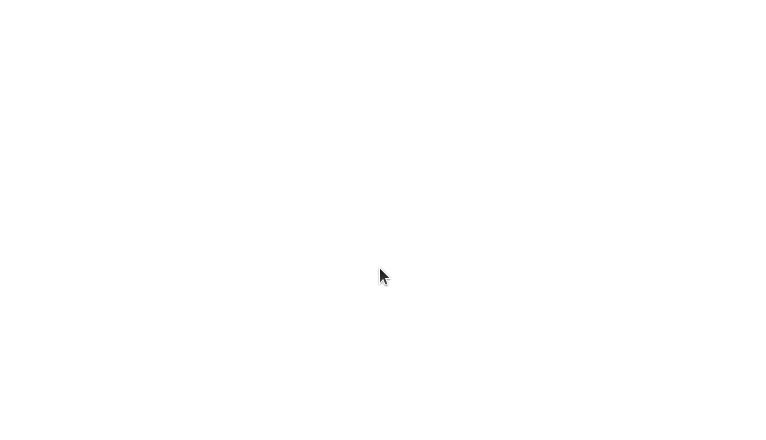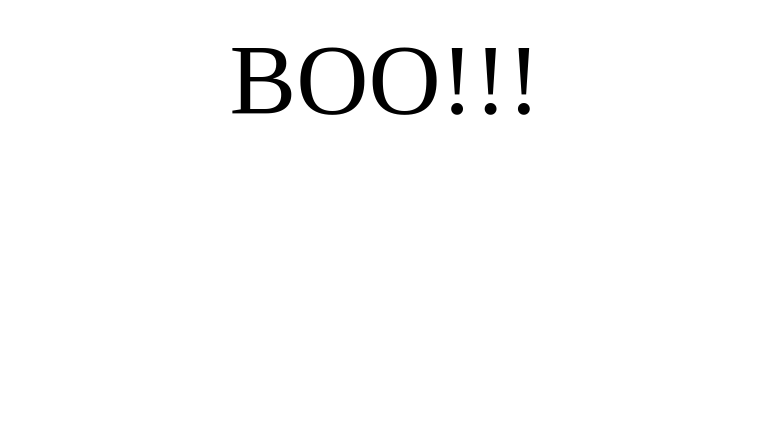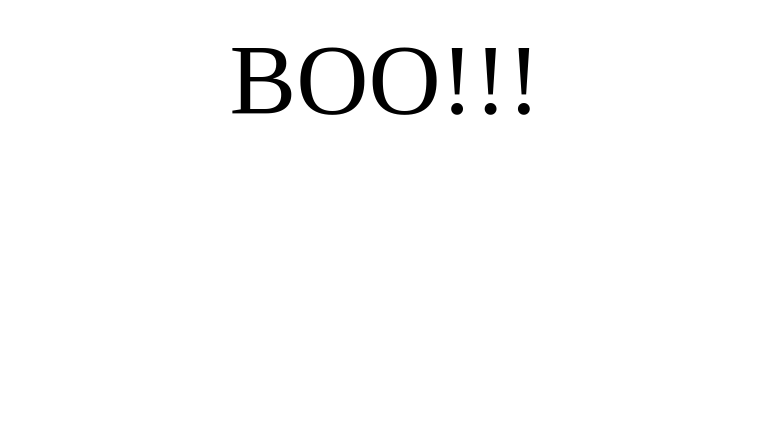
def show_boo_text():
boo_text = add_text("BOO!!!", 100)
position_element(boo_text, "center", 300)
set_timeout(show_boo_text, 3)
Example output:
update_text()¶
Changes the text in text_element to the new_text.
Function signature:
update_text(text_element, new_text)
Parameters:
text_element(element): The element to adjust.new_text(str): The new text for thetext_element.
Example usage:
def update_text_element():
update_text(text_element, "Updated text")
text_element = add_text("Original text", 32)
position_element(text_element, "center", 400)
update_text_button = add_button("Update Text")
position_element(update_text_button, "center", "center")
click(update_text_button, update_text_element)
Example output:

remove_element()¶
Removes the element from the page.
Function signature:
remove_element(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to remove.
Example usage:
def remove_taco():
remove_element(taco_image)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 200)
position_element(taco_image, "center", 300)
remove_taco_button = add_button("Remove Taco")
position_element(remove_taco_button, "center", "center")
click(remove_taco_button, remove_taco)
Example output:

rotate_element()¶
Rotates the element by the given number of degrees.
Function signature:
rotate_element(element, degrees)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to rotate.degrees(int): The number of degrees to rotate theelement.
Example usage:
def rotate_taco():
rotate_element(taco_image, 180)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 200)
position_element(taco_image, "center", 300)
rotate_taco_button = add_button("Rotate Taco")
position_element(rotate_taco_button, "center", "center")
click(rotate_taco_button, rotate_taco)
Example output:

vanish()¶
Removes the element from the page over a 1 second interval.
Function signature:
vanish(element)
Parameters:
element(element): The element to remove.
Example usage:
def vanish_taco():
vanish(taco_image)
taco_image = add_image("taco.jpg", 200)
position_element(taco_image, "center", 300)
vanish_taco_button = add_button("Vanish Taco")
position_element(vanish_taco_button, "center", "center")
click(vanish_taco_button, vanish_taco)
Example output:
